吴恩达2022新版机器学习-week3-逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
逻辑回归
实际上用于分类问题中(不要被名字迷惑),其输出值在0-1之间 这里采用sigmoid作为model,公式如下: $g(z)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-z}}$ model: $f(\vec{w},b)(\vec{x}) = g(\vec{w}\cdot{\vec{x}}+b) = \frac{1}{1+e^{-(\vec{w}\cdot{\vec{x}}+b)}}$
逻辑回归的Loss Function
损失函数只是在单个数据集中
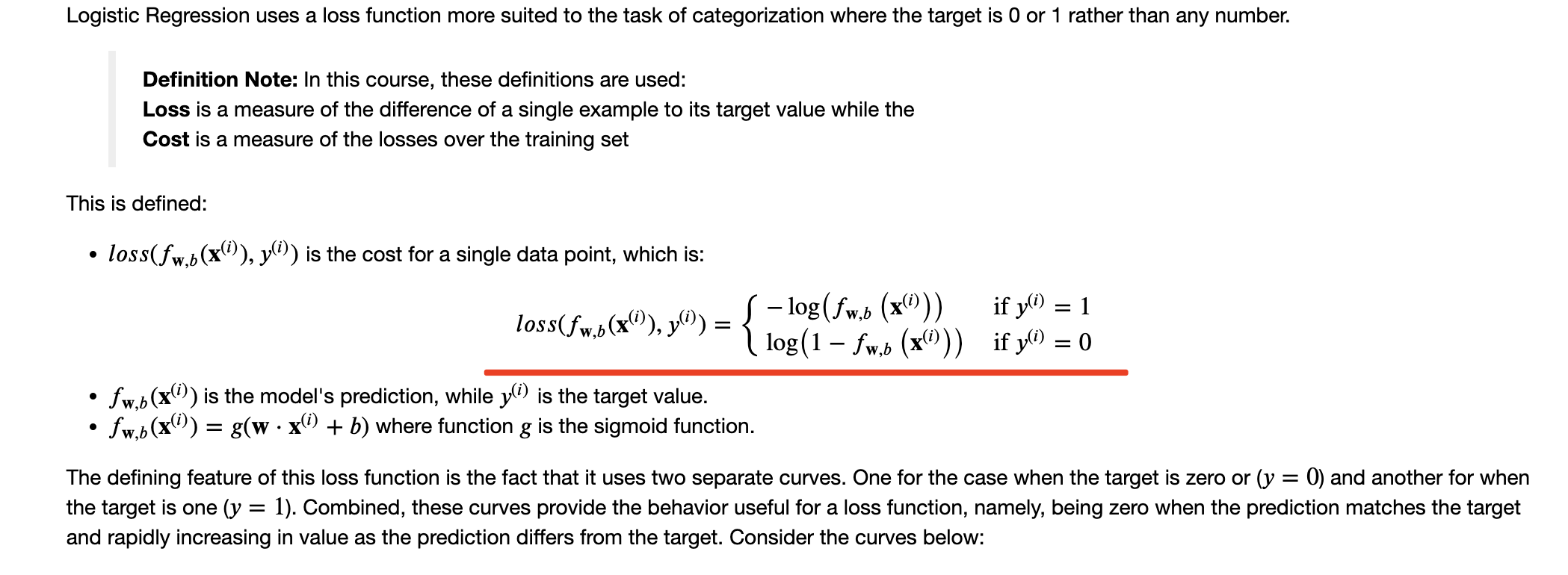

逻辑回归的Cost Function
需要对loss求和累加
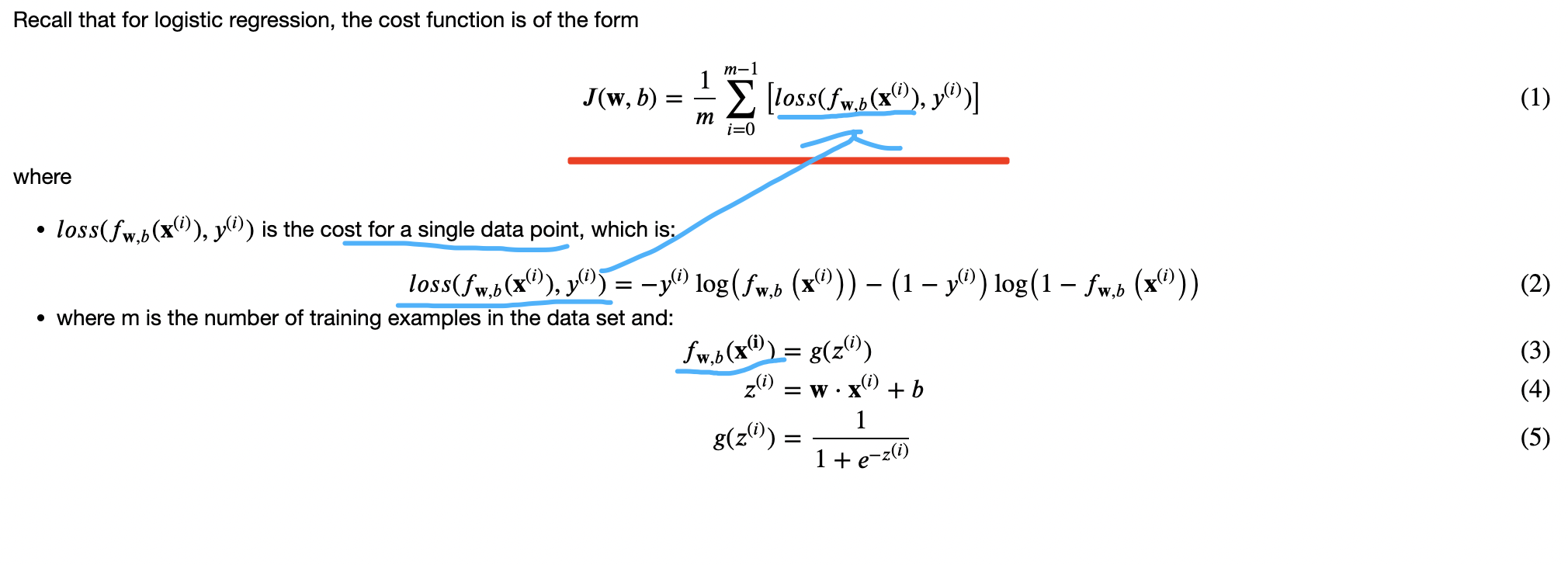
比如:
|
|
逻辑回归的Gradient Descent
跟线性回归一样,只不过f的内容有些区别
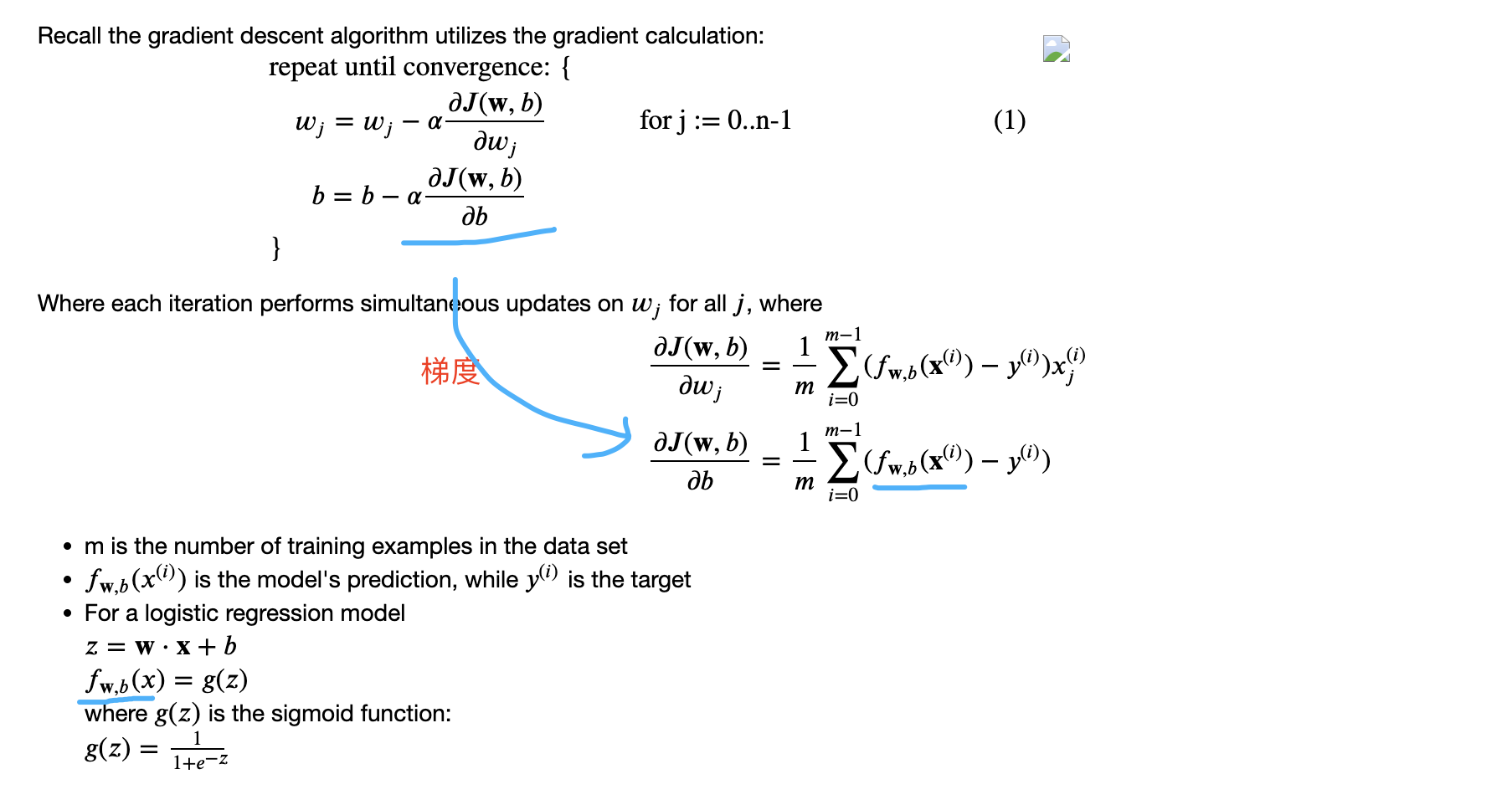
$$\begin{align*} &\text{repeat until convergence:} ; \lbrace \ & ; ; ;w_j = w_j - \alpha \frac{\partial J(\mathbf{w},b)}{\partial w_j} \tag{1} ; & \text{for j := 0..n-1} \ & ; ; ; ; ;b = b - \alpha \frac{\partial J(\mathbf{w},b)}{\partial b} \ &\rbrace \end{align*}$$
Where each iteration performs simultaneous updates on $w_j$ for all $j$, where $$\begin{align*} \frac{\partial J(\mathbf{w},b)}{\partial w_j} &= \frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i = 0}^{m-1} (f_{\mathbf{w},b}(\mathbf{x}^{(i)}) - y^{(i)})x_{j}^{(i)} \tag{2} \ \frac{\partial J(\mathbf{w},b)}{\partial b} &= \frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i = 0}^{m-1} (f_{\mathbf{w},b}(\mathbf{x}^{(i)}) - y^{(i)}) \tag{3} \end{align*}$$
计算梯度:
|
|
梯度下降:
|
|
用Scikit-Learn实现逻辑回归
|
|
Overfitting
高方差(high variance)
过拟合$h(\theta)$的多项式过于复杂以致于拟合了所有的数据
解决办法:
- 收集更多训练数据
- 使用更少特征
- 交叉验证
- 早停
- 正则化(正则化可用于降低模型的复杂性。这是通过惩罚损失函数完成的,可通过 L1 和 L2 两种方式完成)
- Dropout(Dropout 是一种正则化方法,用于随机禁用神经网络单元。它可以在任何隐藏层或输入层上实现,但不能在输出层上实现。该方法可以免除对其他神经元的依赖,进而使网络学习独立的相关性。该方法能够降低网络的密度)
这里以正则化说了:
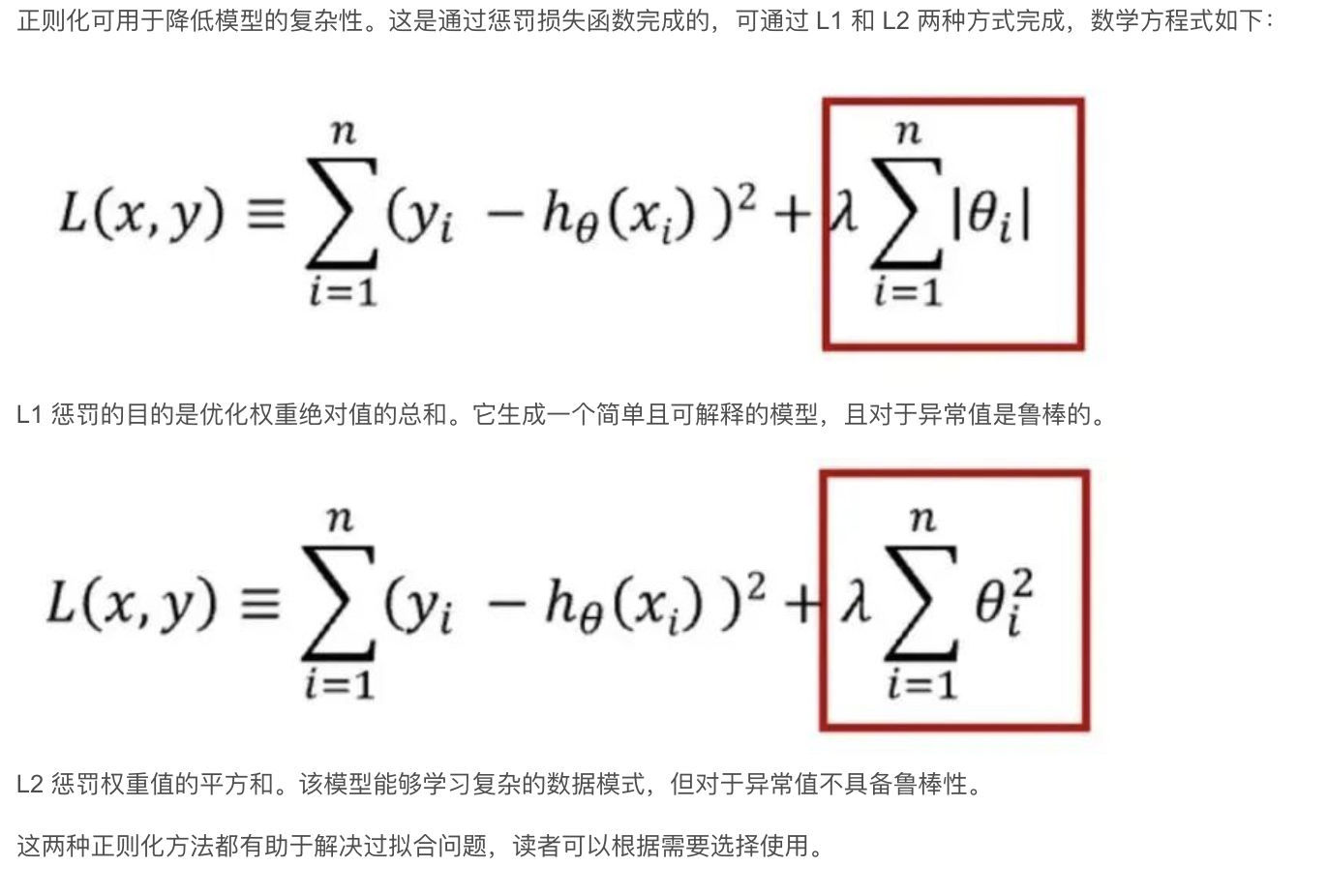
正则化可以防止过拟合,进而增强泛化能力 采取的方法是在原来平方差误差的基础上添加正则项(一般选择正则化w而非b):
线性回归:
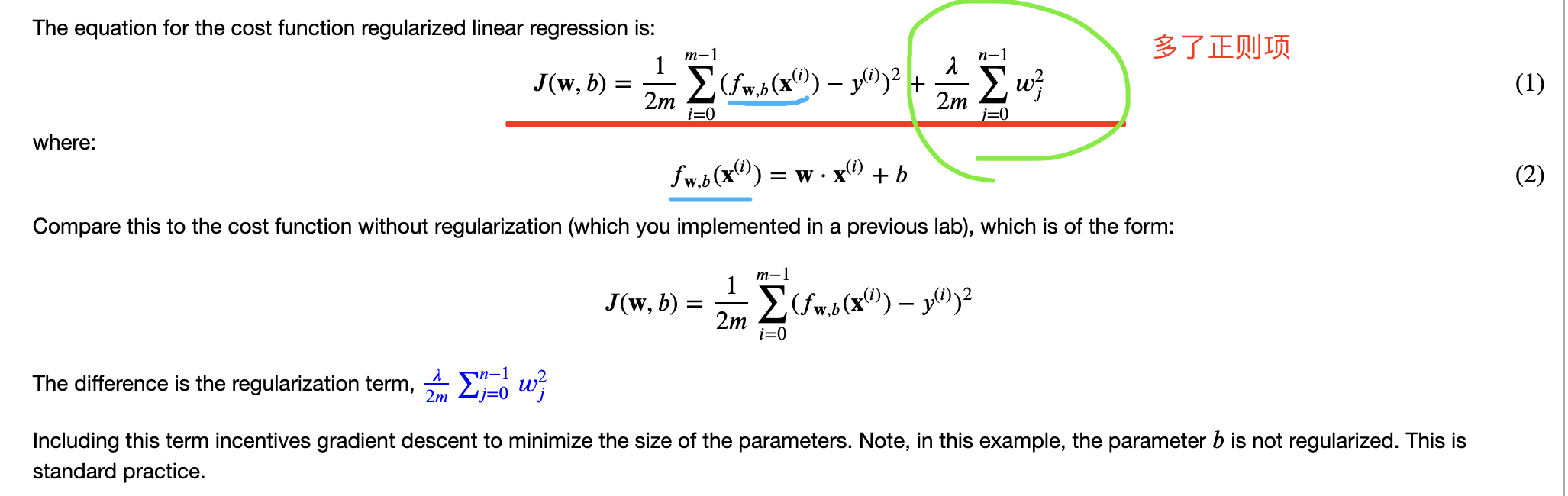
|
|
逻辑回归添加正则项:
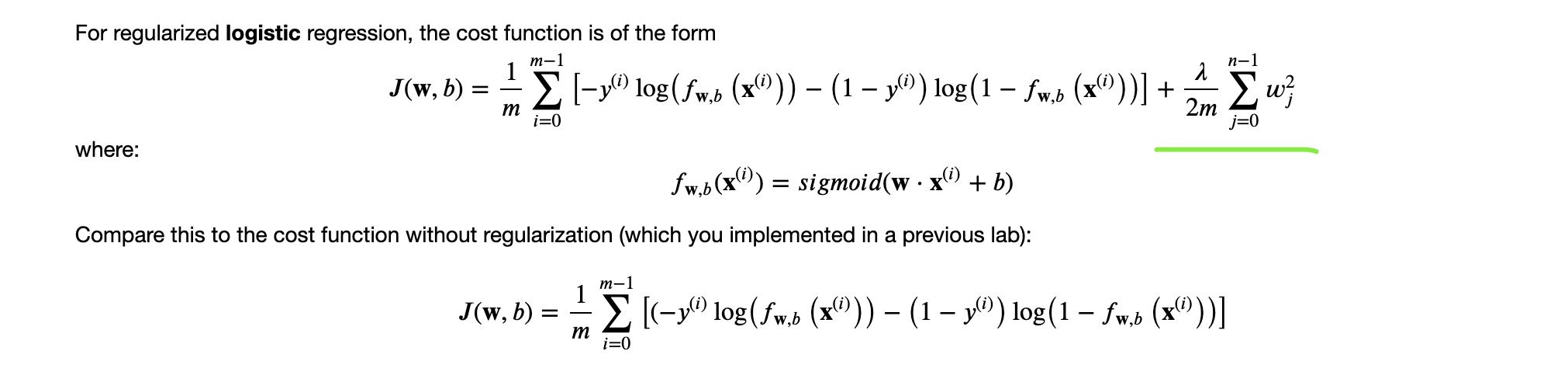
|
|
梯度下降中添加正则项:
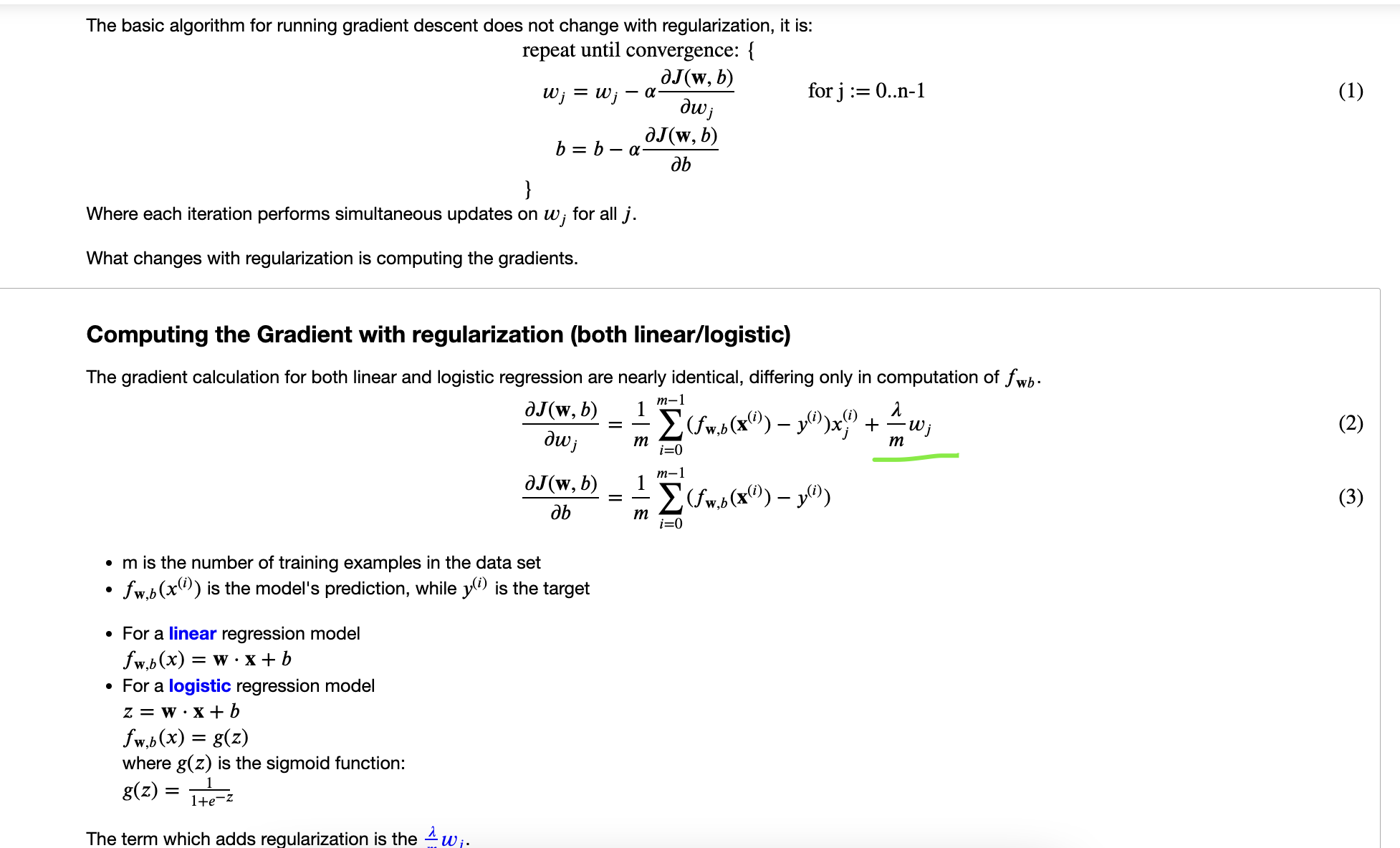
|
|