前言
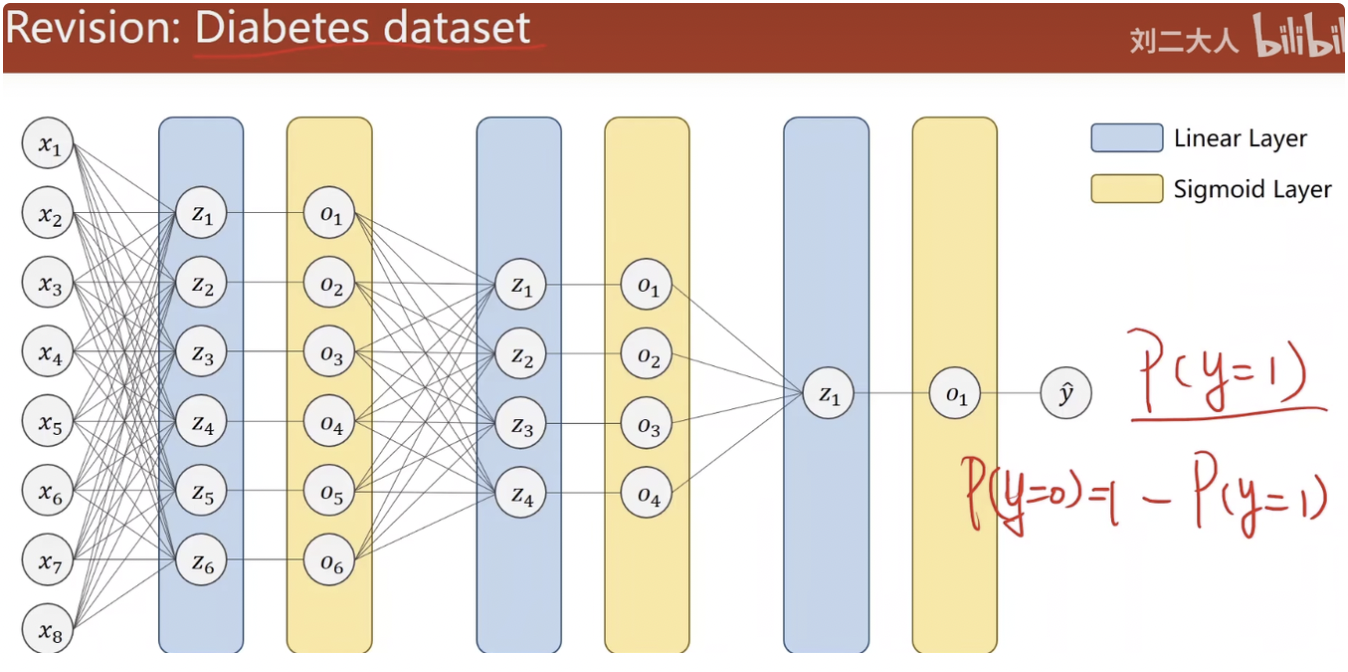
回顾之前糖尿病的问题,是二分类的,但实际中二分类很少见,大多是手写数字识别等多分类问题
 下文以MINIST为例进行分析
下文以MINIST为例进行分析
网络设计
转为二分类
如何使用sigmoid来实现手写数字识别?
把每一个分类作为二分类进行判断。
eg:当输出为1时,对其他的非1输出都规定为0,以此来进行判断

但这种情况下,类别之间所存在的互相抑制的关系没有办法体现,当一个类别出现的概率较高时,其他类别出现的概率仍然有可能很高。
换言之,当计算输出为1的概率之后,再计算输出为2的概率时,并不是在输出为非1的条件下进行的,也就是说,所有输出的概率之和实际上是大于1的
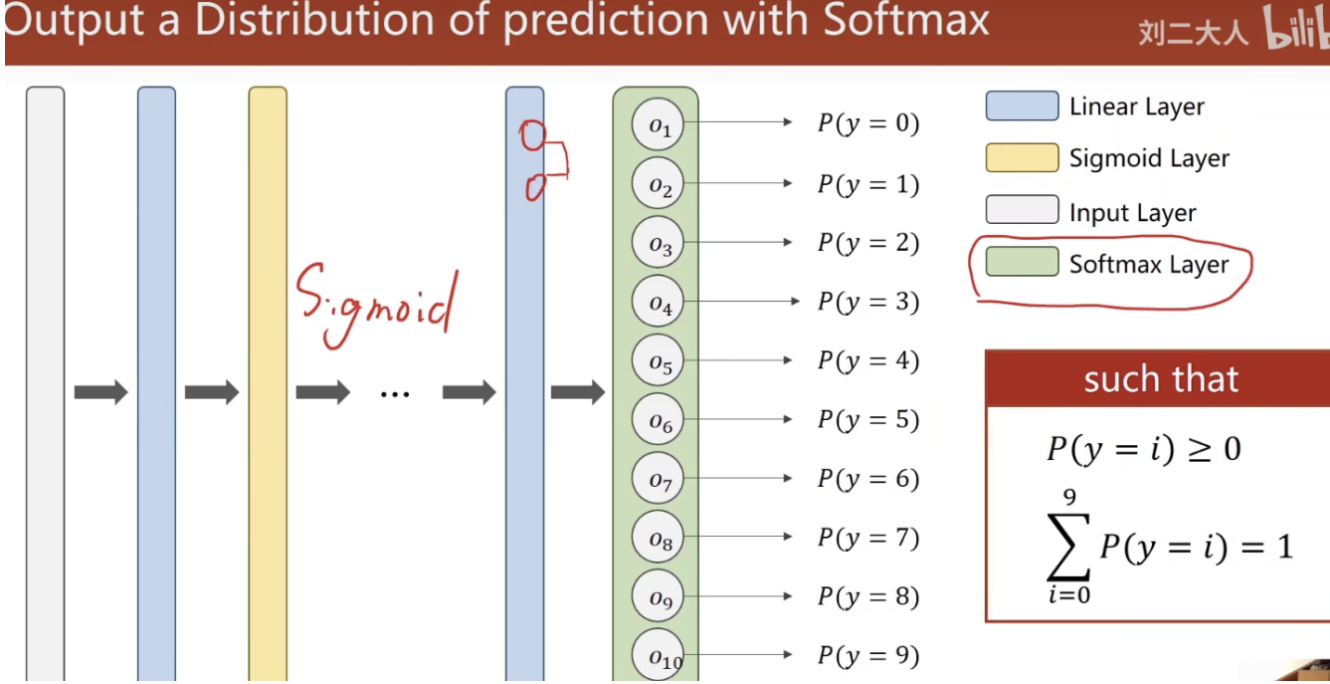
对于一个多分类问题,其解决方案应该基于如下要求,满足是一个分布:
改进的网络
使用Softmax层来实现多分类。

假定$Z^l$为最后一层线性层的输出,$Z_i$为第i类的输出。则最终的softmax层函数应为:
$$
P(y=i) = \frac{e^{z_i}}{\sum^{K-1}_{j=0}{e^{z_j}}}, i \in {0,\dots,K-1}
$$

损失函数
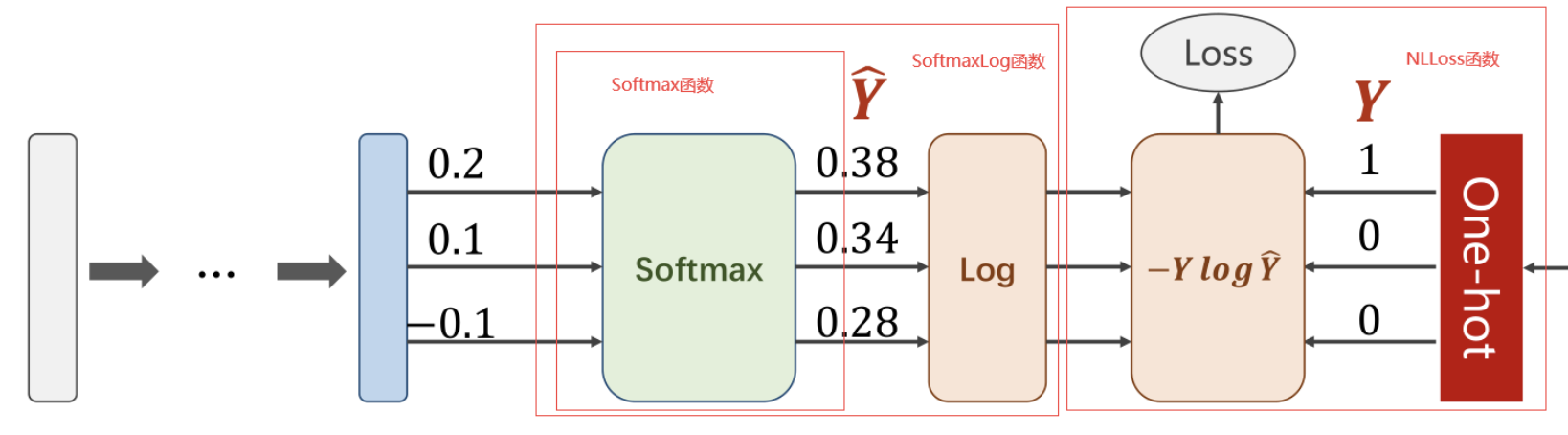
交叉熵的计算公式如下:
$$
H(P,Q) =-\sum^n_{i=1} P(X_i)log(Q(X_i))
$$
在多分类问题中,该公式可扩展为:
$$
H(P,Q) =-\sum^n_{i=1}\sum^m_{j=1} P(X_{ij})log(Q(X_{ij}))
$$
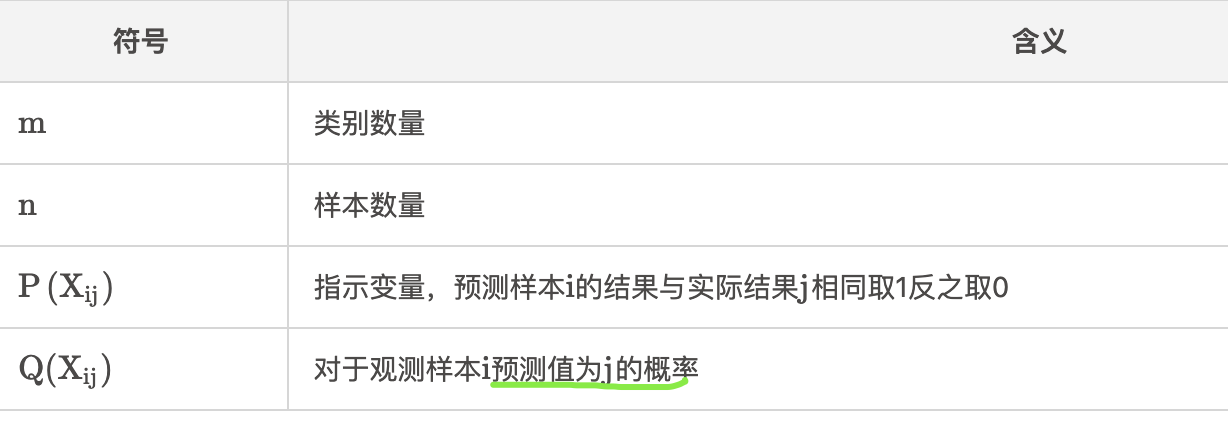
符号:

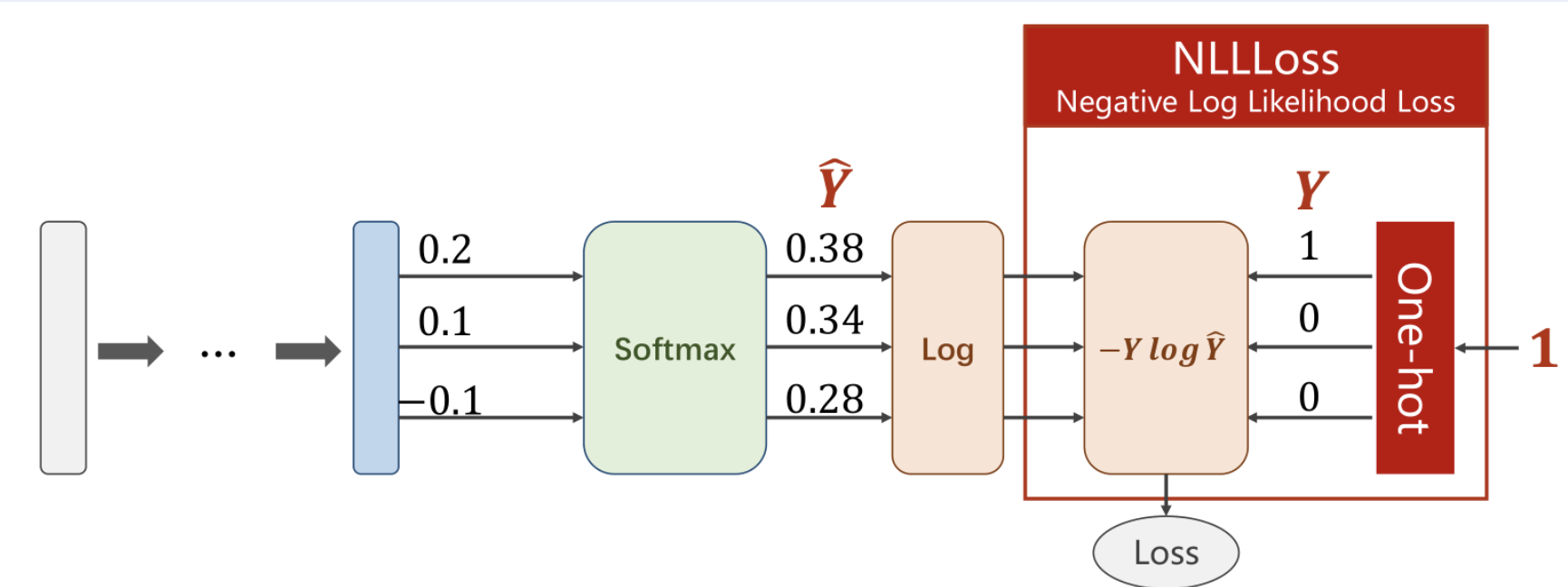
一个样本所有分类的loss计算过程可以简化为
$$
Loss = -log(P(X)) = -Ylog \widehat Y
$$
其中,$X$表示事件预测值与实际值相同,$Y$表示非0即1的指示变量,$\widehat Y$表示Softmax的输出。
此时$Y$其实是作为独热编码(One-hot)输入的,以对离散的变量进行分类。即只在实际值处为1,其他均为0.

代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
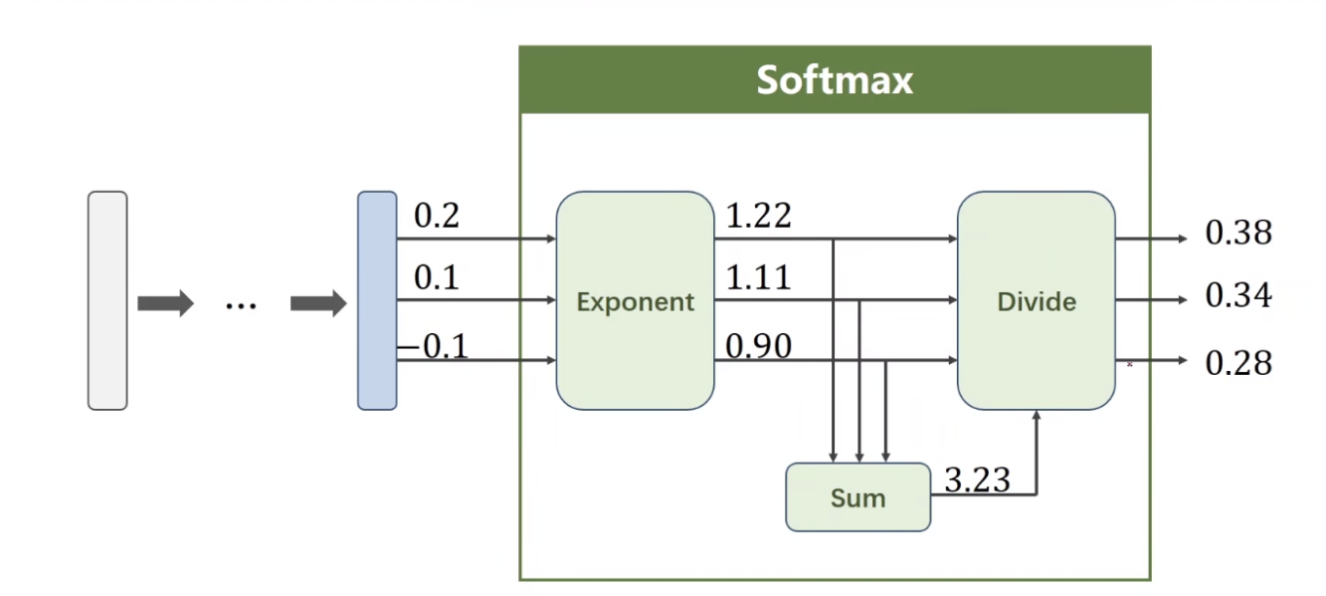
import numpy as np
y = np.array([1, 0, 0])
z = np.array([0.2, 0.1, -0.1])
y_pred = np.exp(z) / np.exp(z).sum()
loss = (-y*np.log(y_pred)).sum()
print(loss)
|
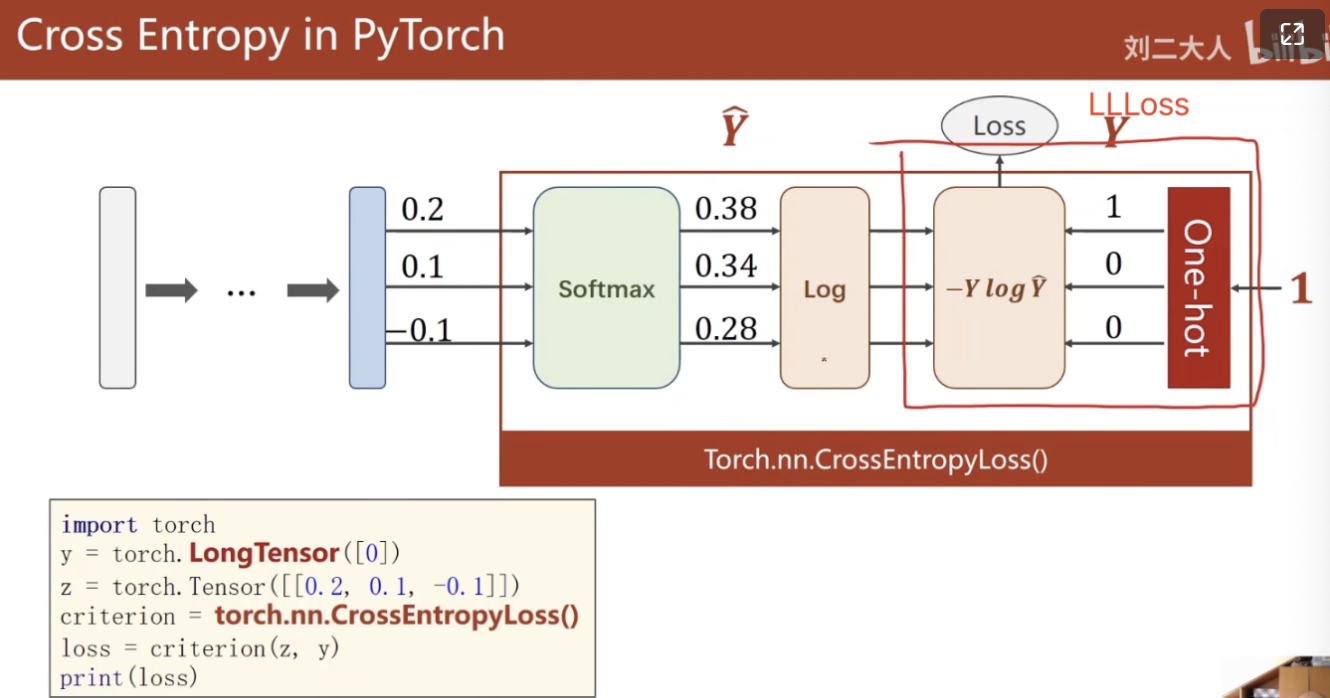
上述代码封装在CrossEntropyLoss()函数中,如下图CrossEntropyLoss()包含了下面好几步:

在PyTorch中可写成这样:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
import torch
# 需要LongTensor
y = torch.LongTensor([0])
z = torch.Tensor([[0.2,0.1,-0.1]])
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # pytorch中最后一层交给CrossEntropyLoss()就行,不需要激活,CrossEntropyLoss包含上图括号里面的好几步。
loss = criterion(z,y)
print(loss)
|
区分:NLLLoss与CrossEntropyLoss
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.NLLLoss.html#torch.nn.NLLLoss
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss.html#torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss
CrossEntropyLoss <===> NLLLoss + LogSoftmax
nn.LogSoftmax:
softmax常用在网络的输出层上,以得到每个类别的概率,顾名思义,nn.LogSoftmax就是对softmax的结果取了一个log。
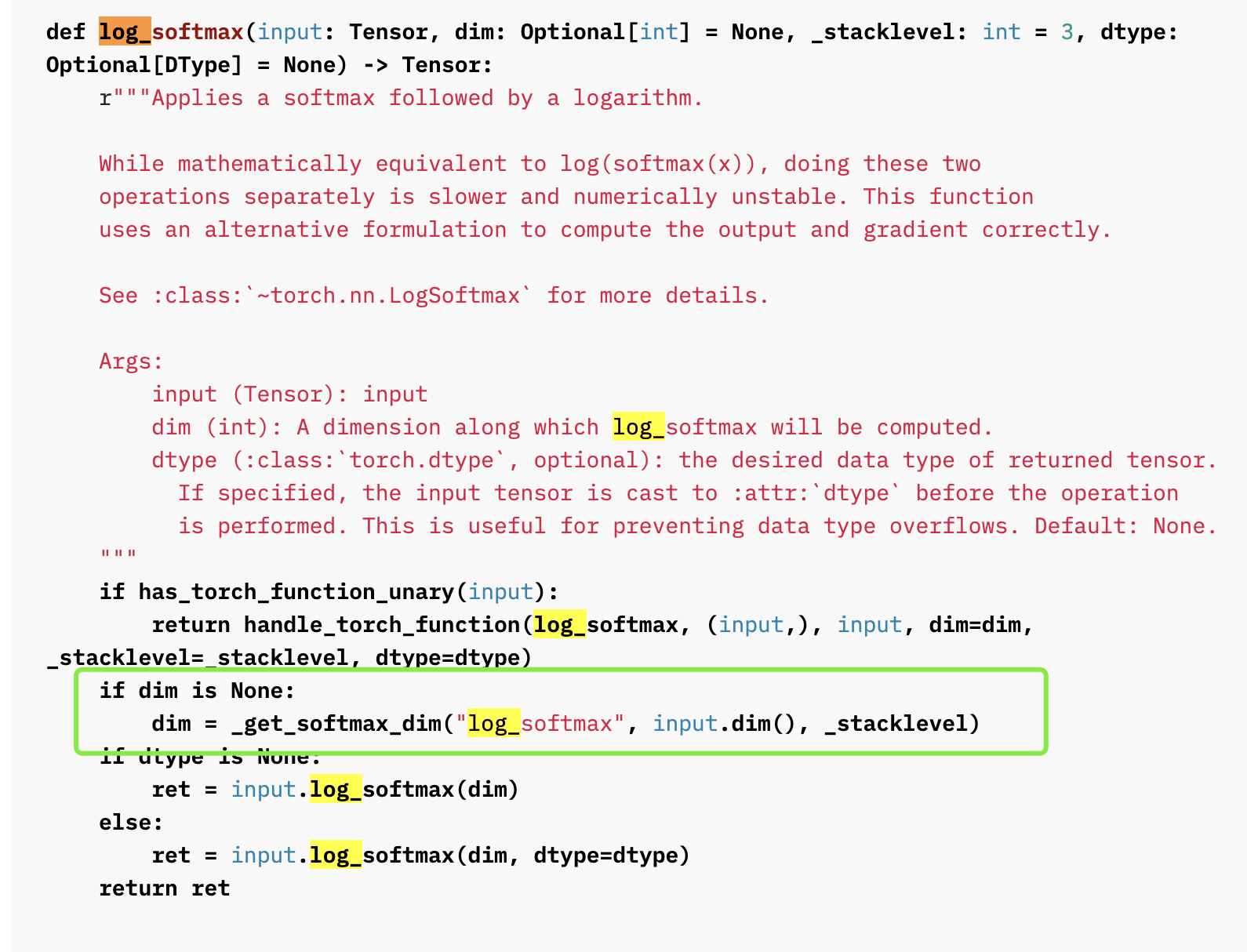
 使用这个类时最好要指定dim,即沿着tensor的哪一个维度做softmax,如果不指定,也能做,那么沿着哪一维做呢?通过层层查看源码,我们发现:
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torch/nn/functional.html#log_softmax
使用这个类时最好要指定dim,即沿着tensor的哪一个维度做softmax,如果不指定,也能做,那么沿着哪一维做呢?通过层层查看源码,我们发现:
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torch/nn/functional.html#log_softmax
 如果不指定dim,torch会调用到
如果不指定dim,torch会调用到_get_softmax_dim函数,该函数会根据输入tensor的维度总数指定一个,0、1、3维tensor,沿着第0维做;其他的,沿着第1维做。同时,该函数给我们了警告,告诉我们应该人为指定dim.

nn.NLLLoss:
全称叫负对数似然loss(negative log likelihood loss)
 因为它要求输入就已经是每个类的对数值了。值得注意的是,target并不是one-hot向量,而是范围在[0, C-1]之间的类别索引。这一点和后面要说的CrossEntropyLoss是一样的。
因为它要求输入就已经是每个类的对数值了。值得注意的是,target并不是one-hot向量,而是范围在[0, C-1]之间的类别索引。这一点和后面要说的CrossEntropyLoss是一样的。
nn.CrossEntropyLoss
nn.CrossEntropyLoss可以看作是nn.LogSoftmax和nn.NLLLoss的结合,即对输入数据先做log_softmax,再过NLLLoss。


实例:手写数字识别
MINIST数据集中每个数字都是一个$28*28=784$大小的灰度图,将灰度图中的每个像素值映射到$(0,1)$区间内,可以进行映射。


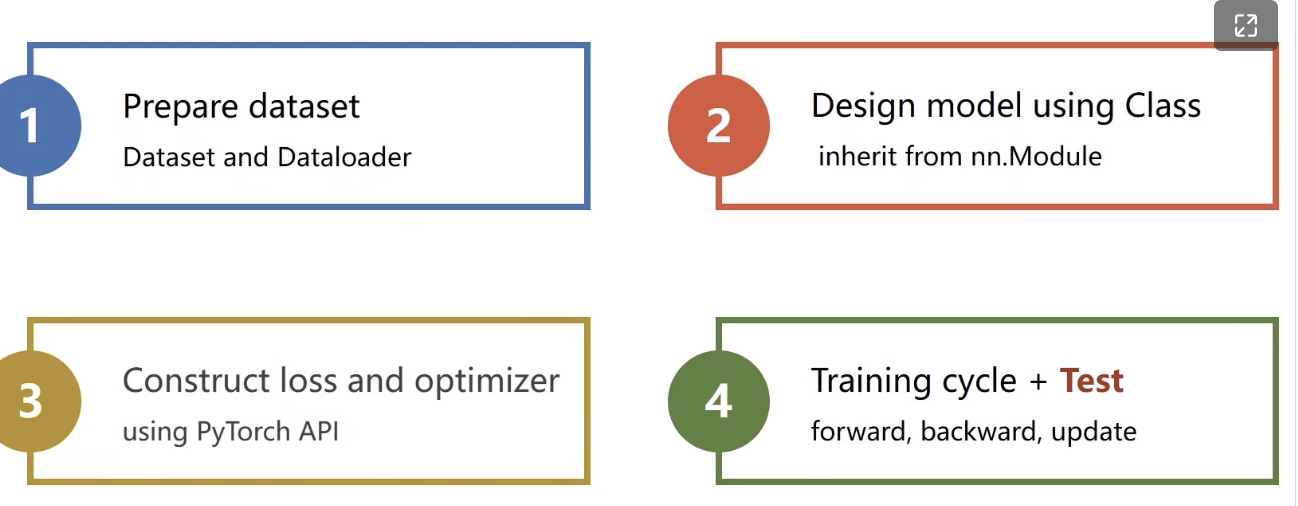
步骤:

模型如下:

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
|
"""
多分类问题
手写数字识别
"""
## 1.导包
import torch
# 组建DataLoader
from torchvision import transforms #图像
from torchvision import datasets
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
# 激活函数和优化器
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
## 2.数据准备
# Dataset&Dataloader必备
bacth_size = 64
# pillow(PIL)读的原图像格式为W*H*C,原值较大-->转为格式为C*W*H值为0-1的Tensor
transform = transforms.Compose([
# 变为格式为C*W*H的Tensor
transforms.ToTensor(),
# 第一个是均值,第二个是标准差,变值为0-1
transforms.Normalize((0.1307, ), (0.3081, ))
])
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data/mnist/', train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=bacth_size)
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data/mnist/', train=False, download=True, transform = transform)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, shuffle=False, batch_size=bacth_size)
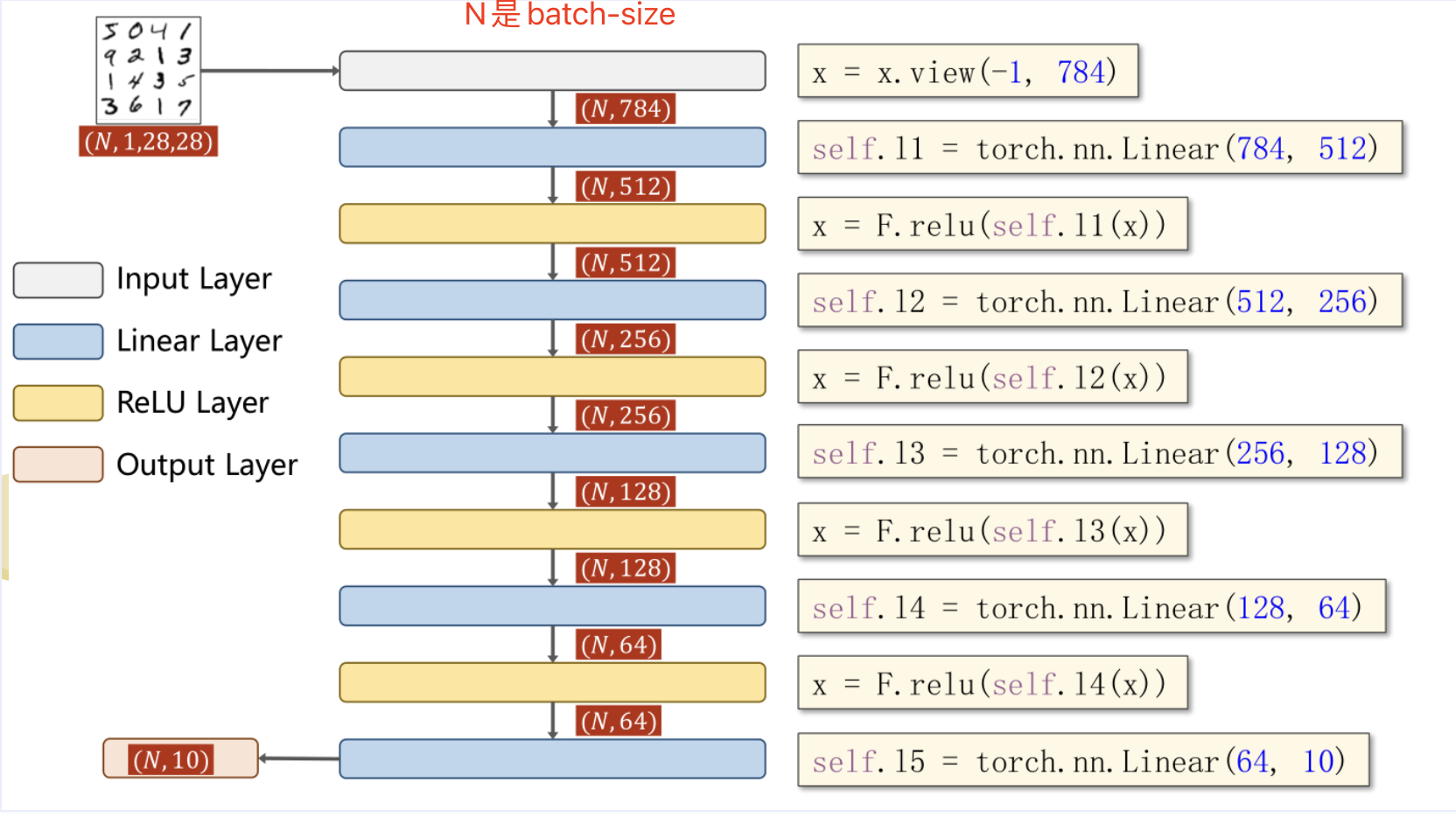
## 3.模型设计
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# 线性层1,input784维 output512维
self.l1 = torch.nn.Linear(784, 512)
self.l2 = torch.nn.Linear(512, 256)
self.l3 = torch.nn.Linear(256, 128)
self.l4 = torch.nn.Linear(128, 64)
# 线性层5,input64维 output10维
self.l5 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# 改变张量形状view() / reshape
# view 只能用于内存中连续存储的Tensor,transpose / permute之后的不能用
# 变为二阶张量(矩阵),-1用于计算填充batch_size
x = x.view(-1, 784)
# relu 激活函数
x = F.relu(self.l1(x))
x = F.relu(self.l2(x))
x = F.relu(self.l3(x))
x = F.relu(self.l4(x))
# 第五层不再进行relu激活
return self.l5(x)
model = Net()
## 4.损失和优化器
# 交叉熵损失
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 随机梯度下降,momentum表冲量,在更新时一定程度上保留原方向
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.5)
## 5.训练和测试
def train(epoch):
running_loss = 0.0
# 提取数据
for batch_idx, data in enumerate(train_loader, 0):
inputs, target = data
# 优化器清零
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 前馈+反馈+更新
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 累计loss
running_loss += loss.item()
if batch_idx % 300 == 299:
print('[%d, %5d] loss: %.3f' % (epoch + 1, batch_idx + 1, running_loss / 300))
running_loss = 0.0
def test():
correct = 0
total = 0
# 避免计算梯度
with torch.no_grad():
for data in test_loader:
images, labels = data
outputs = model(images)
# 取每一行(dim=1表第一个维度)最大值(max)的下标(predicted)及最大值(_)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, dim=1)
# 加上这一个批量的总数(batch_size),label的形式为[N,1]
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
print('Accuracy on test set: %d %%' % (100 * correct / total))
if __name__ == '__main__':
for epoch in range(10):
train(epoch)
test()
|
课后题
https://www.kaggle.com/c/otto-group-product-classification-challenge
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
|
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
# 定义函数将类别标签转为id表示,方便后面计算交叉熵
def lables2id(lables):
target_id = []
target_lables = ['Class_1', 'Class_2', 'Class_3', 'Class_4', 'Class_5', 'Class_6', 'Class_7', 'Class_8', 'Class_9']
for lable in lables:
target_id.append(target_lables.index(lable))
return target_id
# 定义数据集类
class ProductDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self,filepath):
data = pd.read_csv(filepath)
lables = data['target']
self.len = data.shape[0] # shape(多少行,多少列)
self.x_data = torch.tensor(np.array(data)[:,1:-1].astype(float))
self.y_data = lables2id(lables)
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.x_data[index], self.y_data[index]
def __len__(self):
return self.len
dataset = ProductDataset('./otto-group-product-classification-challenge/train.csv')
# 建立数据集加载器
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(93, 64)
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(64, 32)
self.linear3 = torch.nn.Linear(32, 16)
self.linear4 = torch.nn.Linear(16, 9)
self.relu = torch.nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(self.linear1(x))
x = self.relu(self.linear2(x))
x = self.relu(self.linear3(x))
x = self.linear4(x)
return x
def predict(self, x):
with torch.no_grad():
x = self.relu(self.linear1(x))
x = self.relu(self.linear2(x))
x = self.relu(self.linear3(x))
x = self.relu(self.linear4(x))
# 这里先取出最大概率的索引,即是所预测的类别。
_, predicted = torch.max(x, dim=1)
# 将预测的类别转为one-hot表示,方便保存为预测文件。
y = pd.get_dummies(predicted)
return y
model = Net()
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.5)
def train(epoch):
running_loss = 0.0
for batch_idx, data in enumerate(train_loader):
inputs, target = data
inputs = inputs.float()
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
if batch_idx % 300 == 299:
print('[%d, %5d] loss: %.3f' % (epoch+1, batch_idx+1, running_loss/300))
running_loss = 0.0
# 开始训练
if __name__ == '__main__':
for epoch in range(100):
train(epoch)
# 定义预测保存函数,用于保存预测结果。
def predict_save():
test_data = pd.read_csv('./otto-group-product-classification-challenge/test.csv')
test_inputs = torch.tensor(np.array(test_data)[:,1:].astype(float))
out = model.predict(test_inputs.float())
lables=['Class_1', 'Class_2', 'Class_3', 'Class_4', 'Class_5', 'Class_6', 'Class_7', 'Class_8', 'Class_9']
# 添加列标签
out.columns = lables
# 插入id行
out.insert(0,'id',test_data['id'])
output = pd.DataFrame(out)
output.to_csv('my_predict.csv', index=False)
predict_save()
|
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/cjf1699/article/details/122963613
 下文以MINIST为例进行分析
下文以MINIST为例进行分析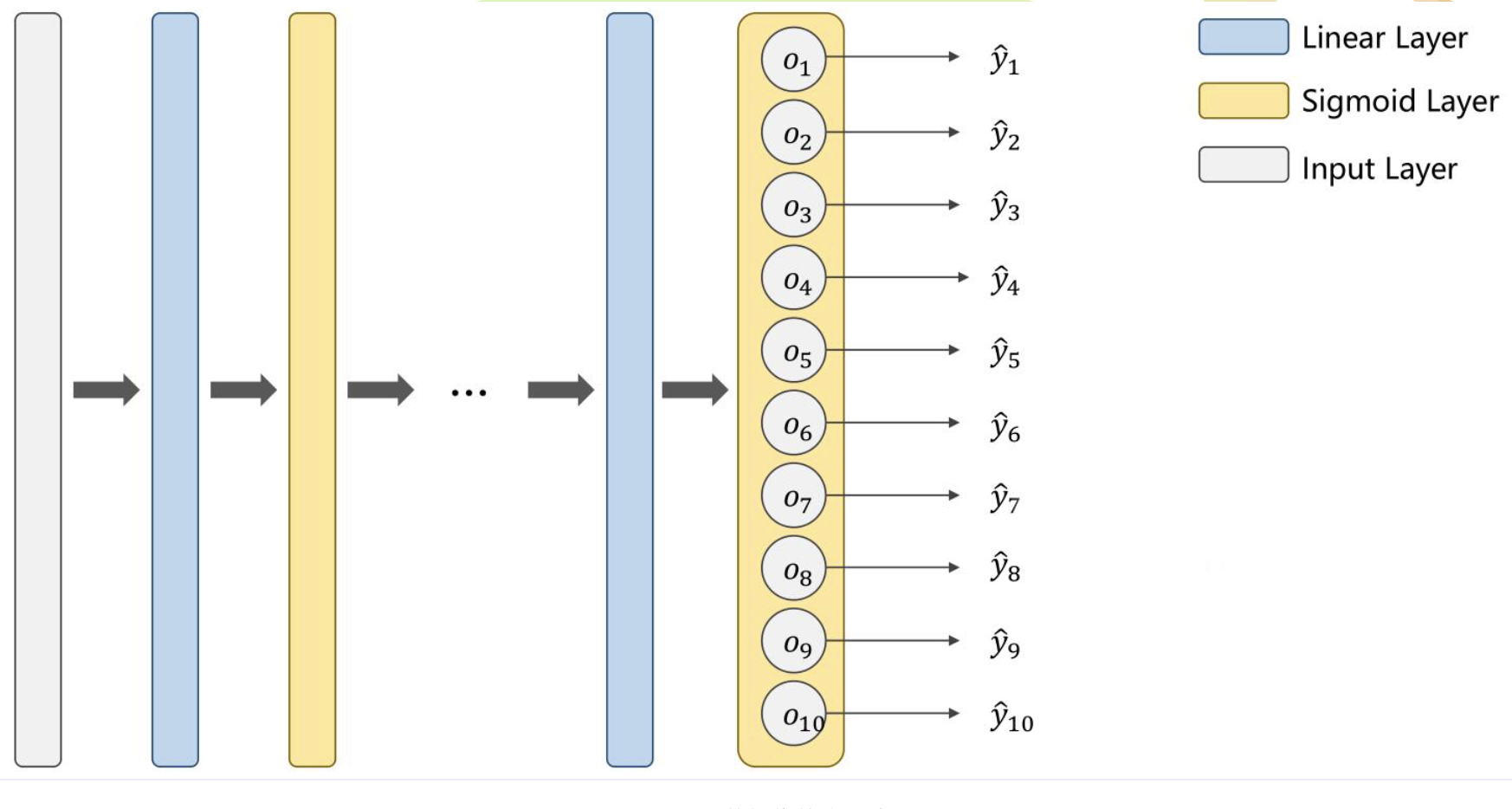
 使用这个类时最好要指定dim,即沿着tensor的哪一个维度做softmax,如果不指定,也能做,那么沿着哪一维做呢?通过层层查看源码,我们发现:
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torch/nn/functional.html#log_softmax
使用这个类时最好要指定dim,即沿着tensor的哪一个维度做softmax,如果不指定,也能做,那么沿着哪一维做呢?通过层层查看源码,我们发现:
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torch/nn/functional.html#log_softmax
 如果不指定dim,torch会调用到
如果不指定dim,torch会调用到
 因为它要求输入就已经是每个类的对数值了。值得注意的是,target并不是one-hot向量,而是范围在[0, C-1]之间的类别索引。这一点和后面要说的CrossEntropyLoss是一样的。
因为它要求输入就已经是每个类的对数值了。值得注意的是,target并不是one-hot向量,而是范围在[0, C-1]之间的类别索引。这一点和后面要说的CrossEntropyLoss是一样的。