1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
# 最前面跟GoogleNet的b1是一样的
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1))
def resnet_block(in_channels, out_channels, num_residuals, first_block=False):
if first_block: # 第一个要特殊处理
assert in_channels == out_channels # 第一个模块的通道数同输入通道数一致
blk = []
for i in range(num_residuals):
# 需要注意first_block已经做了3*3的最大池化,所以没必要做变换.第二层,第三层,第四层跳跃连接时,维度不同,需要先经过1*1卷积变换再相加。
if i == 0 and not first_block:
# 每一个block有2个esidual,每一个Residual有2个卷积层
blk.append(Residual(in_channels, out_channels, use_1x1conv=True, stride=2)) # 减半
else:
blk.append(Residual(out_channels, out_channels))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
# 为ResNet加入所有残差块
net.add_module("resnet_block1", resnet_block(64, 64, 3, first_block=True)) # 第一个高宽不变
net.add_module("resnet_block2", resnet_block(64, 128, 4)) # 下面三个:重复两个block,通道数加倍,高宽减半
net.add_module("resnet_block3", resnet_block(128, 256, 6)) # 自己可以设置每个里面有多少个block,这里设置的是2
net.add_module("resnet_block4", resnet_block(256, 512, 3))
# 最后,与GoogLeNet一样,加入全局平均池化层后接上全连接层输出。
net.add_module("global_avg_pool", nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1))) # GlobalAvgPool2d的输出: (Batch, 512, 1, 1)
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(512, 10))) # 展开,全连接层
# 这里每个模块里有4个卷积层(不计算1×11×1卷积层),
# 加上最开始的卷积层和最后的全连接层,共计18层。
# 这个模型通常也被称为ResNet-18
# 通过配置不同的通道数和模块里的残差块数可以得到不同的ResNet模型,例如更深的含152层的ResNet-152
# 来观察一下输入形状在ResNet不同模块之间的变化。
X = torch.rand((1, 1, 224, 224))
for name, layer in net.named_children():
X = layer(X)
print(name, ' output shape:\t', X.shape)
"""
0 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
1 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
2 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
3 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56])
resnet_block1 output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56])
resnet_block2 output shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 28, 28])
resnet_block3 output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14])
resnet_block4 output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 7, 7])
global_avg_pool output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 1, 1])
fc output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
"""
|
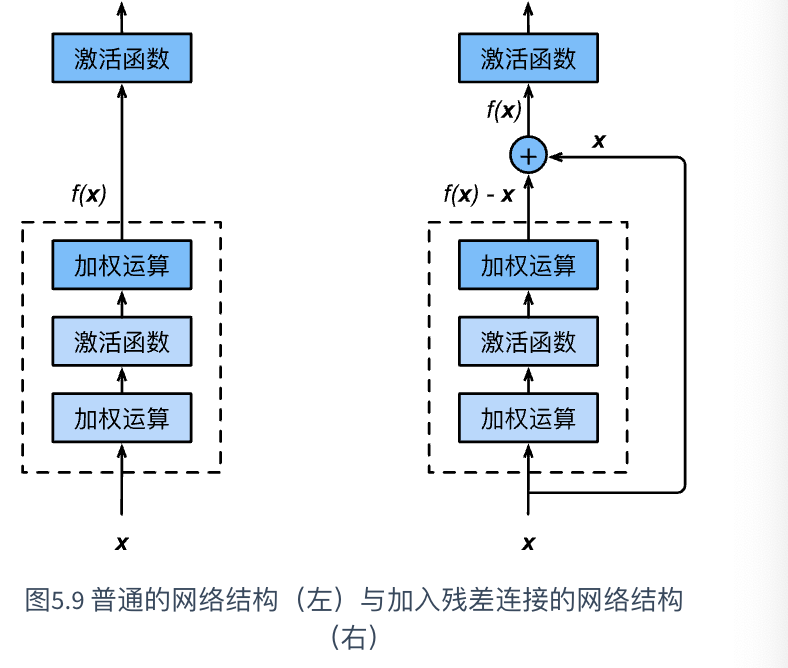
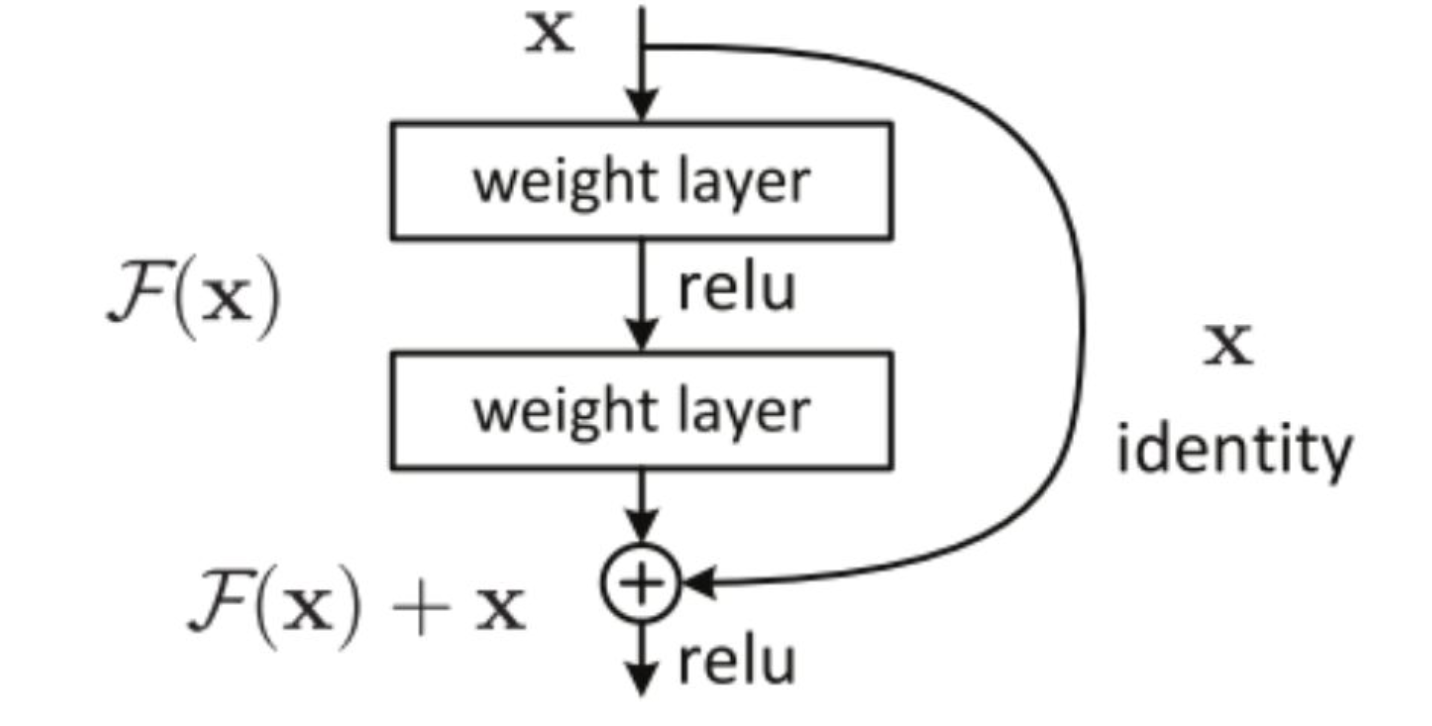 1.恒等映射:
上图中有一个曲线,称为shortcut connection(快捷连接),就是恒等映射。既不增加额外参数,也不增加计算复杂度。而恒等映射表示:输入=输出;
2.图中F(x)的作用:
图中F(x)执行卷积操作,目的是提取图片中的更多特征,或者是其它层没有学习的特征;
1.恒等映射:
上图中有一个曲线,称为shortcut connection(快捷连接),就是恒等映射。既不增加额外参数,也不增加计算复杂度。而恒等映射表示:输入=输出;
2.图中F(x)的作用:
图中F(x)执行卷积操作,目的是提取图片中的更多特征,或者是其它层没有学习的特征;