1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
|
%matplotlib inline
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
n_train, n_test, num_inputs, batch_size = 20, 100, 200, 5
true_w, true_b = torch.ones((num_inputs, 1)) * 0.01, 0.05
# synthetic_data合成数据
train_data = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, n_train)
train_iter = d2l.load_array(train_data, batch_size)
test_data = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, n_test)
test_iter = d2l.load_array(test_data, batch_size, is_train=False)
# 初始化模型参数
def init_params():
w = torch.normal(0,1,size=(num_inputs,1),requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1,requires_grad=True)
return [w,b]
# 定义L2惩罚函数
def l2_penalty(w):
return torch.sum(w.pow(2))/2
# return torch.sum(w**2)/2
def train(lambd):
w, b = init_params()
# 生成一个线性回归函数,损失函数采用平方损失
net, loss = lambda X: d2l.linreg(X, w, b), d2l.squared_loss
num_epochs, lr = 100, 0.003
# 此部分还是绘画模块
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epochs',
ylabel='loss',
yscale='log',
figsize=(6,3),
xlim=[5, num_epochs],
legend=['train', 'test'])
# 依旧是迭代循环
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in train_iter:
with torch.enable_grad():
# 增加了L2范数惩罚项,⼴播机制使l2_penalty(w)成为⼀个⻓度为`batch_size`的向量。
l = loss(net(X), y) + lambd * l2_penalty(w)
l.sum().backward()
d2l.sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size)
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1, (d2l.evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss),
d2l.evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))
# norm是求2范数,item是求数值
print('w的L2范数是:', torch.norm(w).item())
train(0)
# 可以看出有用训练数据较少,出现了严重的过拟合,test函数的loss基本没有下降
train(3)
# 引入L2范数后,test的loss出现了同步下降,有效避免了过拟合
|
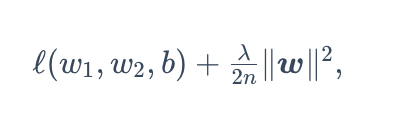 其中超参数λ>0。
当权重参数均为0时,惩罚项最小。
当λ较大时,惩罚项在损失函数中的比重较大,这通常会使学到的权重参数的元素较接近0。
当λ设为0时,惩罚项完全不起作用
其中超参数λ>0。
当权重参数均为0时,惩罚项最小。
当λ较大时,惩罚项在损失函数中的比重较大,这通常会使学到的权重参数的元素较接近0。
当λ设为0时,惩罚项完全不起作用